By Thomas Ultican 1/21/2026
Bellwether’s report is called “How We Solve America’s Math Crisis: A Systemwide Approach to Evidence-Based Math Learning.” The title signals that this is not a serious report. Rather, it is a polemic created with K12 Coalition to sell products. Just like there is no reading crisis in America, there is also no math crisis. However, if these companies can convince enough people a crisis exists, then a pathway for profits opens.
Andrew Rotherham, the founder of Bellwether, is a very energetic and engaged writer who has worked at Time magazine and US News World Report. He was a domestic policy adviser during the Clinton administration and like many Democrats of that era, he bought into the Republican ideology that claimed private business is always superior to any government enterprise. That is why they believe that privatizing prisons and public education is good policy.
Rotherham has served on many boards including The Mind Trust in Indianapolis and ‘The 74’. He has been an advisor to several companies looking to profit from education spending including Whiteboard Advisors; Upbeat, a data analytics company focused on teacher engagement and retention; ClearForce, a security and threat prevention company; and several nonprofit organizations.
Joining Rotherham’s Bellwether to write the “Math Crisis” report is K12 Coalition. The Coalition is one of more than 80 companies owned by the Private Equity firm Quad-C. K12 Coalition recently acquired Keys to Literacy and Professional Development Institute to add to its other organizations like Teaching Channel and Lavinia Group Instructional Support.
These are the companies claiming there is a crisis in math education and that they are the solution.
Not a Crisis
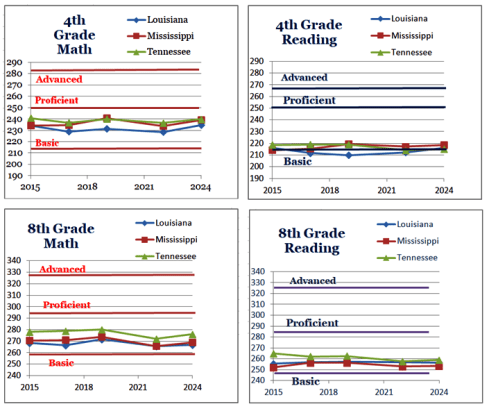
There is not a math crisis and to demonstrate this, let us turn to some national math data available from the federal government.
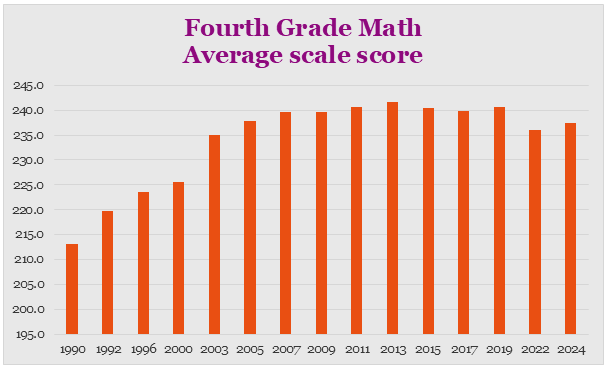
Since 1990, we have been testing fourth grade math. In the early years, schools and teachers gave the tests but were not too concerned about the results. That changed in 2002 with the passage of President Bush’s No Child Left Behind (NCLB). In 2003, the punishment aspect of NCLB caused schools and teachers to focus on improving scores which did dramatically improve.
Most of the gains can be attributed to improved test taking skills and a narrowing of the math curriculum to just items being tested.
In 2022 and 2024, the average scores went down a few points. This is probably the result of two COVID era phenomena. Many schools were closed which meant numerous children missed significant time from school. Once schools were all up and running again absanteeism spiked. Rand corporation recently reported, “Chronic absenteeism in the 2024–2025 school year remained above prepandemic levels.”
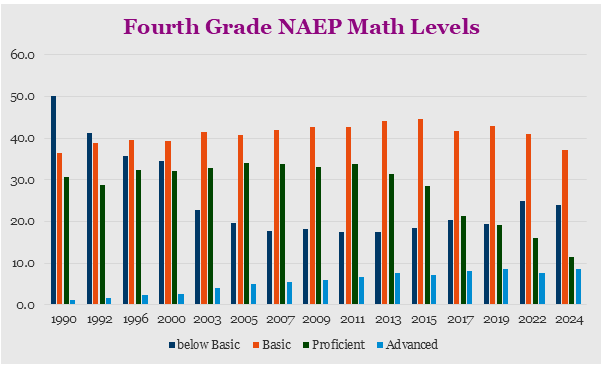
The National Assessment of Education Progress (NAEP) assigns levels to the testing scores; below basic (dark blue), basic (orange), proficient (green) and advanced (light blue). According to Diane Ravitch, basic is about the same as being at grade level and proficient is akin to an A. The advanced level is at the extreme top of the scoring range. Tom Loveless of the Brookings Institute noted, “Even students in private schools, despite hailing from more socioeconomically advantaged homes and in some cases being selectively admitted by schools, fail miserably at attaining NAEP proficiency.”
Since 2003, fourth grade math students have continuously had more than 75% of students scoring at basic or higher.
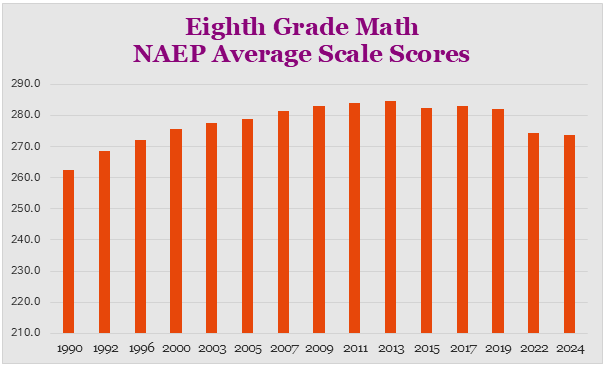
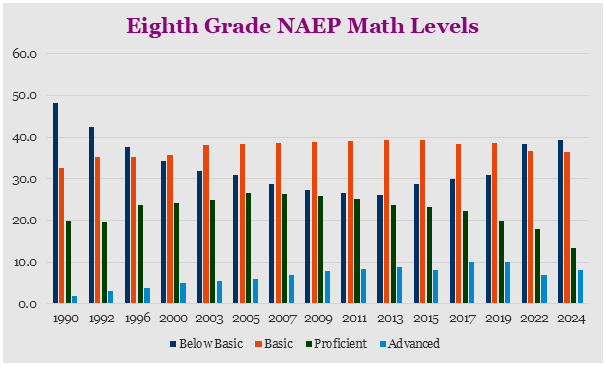
The average NAEP math data for eighth graders showed scores dropping about 7-points from the 2019 results in both 2022 and 2024. Where the fourth graders showed some gain in 2024, the eighth graders did not. A big difference between these two grades is absenteeism. Fourth graders absentee rates for both 2022 and 2024 was about 16%. The eighth grade rates of absenteeism were 23.2% in 2022 and 22.3% in 2024.
If there is a crisis in education, it is not because of the teaching. It is absenteeism which has been a more severe lingering problem since the pandemic.
The chart of eighth grade NAEP levels highlight where the drop in scoring is occurring. Basic level is almost unchanged but below basic has zoomed to levels not seen since the first two administrations in the 1990s. I speculate that the growth in below basic scores ties directly to the students who are not coming to school.
Looking at this data, it becomes very clear that there is no math education crisis in America but there is an absenteeism problem.
The Report
The first line of the report says, “Math achievement across the United States is in crisis, with too many students leaving school without the essential math skills they need to thrive in adulthood.” (Crisis Page 2) This is followed up with their claim that effective math education has three components:
“(1) build educator and student math identity and a shared belief that math is doable, (2) balance conceptual understanding and procedural fluency while also creating meaningful opportunities for real-world application, and (3) ensure that learning progresses logically and cumulatively to deepen knowledge over time.” (Crisis Page 2)
For any math teacher from the last fifty-years and probably more, these three components are old news.
The report claims, “Data demonstrate that when high-quality materials, intentional instructional practices, and strong teacher support are combined, students’ math proficiency can improve significantly.” (Crisis Page 3) Most teachers know that whenever the term “high-quality” is broached, something fishy is afoot. Mostly it indicates marketing is ahead. Reinforcing that marketing is ahead are the following buzz words claiming good math education requires “strong instructional vision, high-quality instructional materials, curricula, professional learning and coaching, and data-driven decision-making.” (Crisis Page 3) The report reader will soon learn where all of this can be purchased.
The report authors sully themselves by stating, “Despite the importance of math, over half of America’s students are not proficient in the subject.”
The report is 34-pages in length. Page 2 which is the first page opens with the claim cited above and Page 3 introduces their three components for effective math education. For pages 3 to 22 the paper is nothing but repetition and obfuscation.
The reader is treated to statements like “The 1983 report A Nation at Risk, commissioned by the Reagan administration, highlighted that a lack of rigor in math education threatened national security and economic strength.” (Crisis Page 8) The reality is that A Nation at Risk was a complete fraud and the National Commission on Excellence in Education knew the answer they wanted before any research was attempted. They believed, with no evidence, that public schools were failing and needed reform.
Finally, we reach the purpose of the report:
“Illustrative Math and ST Math are designed to enhance math instruction with high-quality instructional materials. K12 Coalition’s Lavinia Group Instructional Support offers a comprehensive professional development program designed to help educators foster a culture of excellent math teaching.” (Crisis Page 22)
K12 Coalition and the Lavinia Group Instructional Support are in the business of selling curriculum — which they designate as high-quality — and professional development. From here to page 28, the report is nothing but advertising for these companies. The remainder of their report ends with a short conclusion and the appendix.
Conclusion
It seems alright that a company creates materials to sell its wares. What is not alright is undermining public schools and their legions of fine math educators for that purpose.
Lavina Group sells instructional support, however, the only demand for their product should come from private and charter schools. Privatizing teacher training in the public sector is a bad idea. School districts and local universities have, for more than a century, done this job very well and provided much more value than any private company can afford.



















Recent Comments